The Agile Data Engineer: Role Description
An agile data engineer is anyone who is actively involved with the creation and evolution of the data aspects of one or more software-based solutions. Sometimes called an agile data developer or agile DBA.
The Responsibilities of an Agile Data Engineer
The responsibilities of an agile data engineer vary based on the context of their current environment. For example, in a small organization, they are likely to be a “data jack of all trades”, whereas in a larger organization, they may focus on application development or on data warehouse development. In other words, it depends. The responsibilities potentially include, but are not limited to:
- Working in a manner that reflects their current team(s). Every team is unique, comprised of unique people facing a unique situation. As a result, they will work in a unique manner. Some teams will work in a very agile manner, some in a lean manner, some in a serial manner, or very often a hybrid manner.
- The creation and evolution of documentation. Agile data engineers, like other agile practitioners, can and should take an agile approach to documentation.
- Requirements, architecture, and design exploration. Agile teams take an agile approach to modeling, including data modeling.
- Data source development and evolution.
- Legacy system evolution. Agile data engineers will need to communicate the constraints imposed by legacy data sources, working with application developers to understand those constraints and work appropriately. Agile data engineers will evolve their legacy data schemas over time, applying common data refactorings and data repairs as appropriate.
- Testing. Agile data engineers will work with developers to write and test database code such as stored procedures, data-oriented code within applications that interacts with their data sources.
- Perfomance tuning. Performance tuning, both of the database and of data-oriented code and mappings within applications, is an important aspect of the role.
- Adopt agile database tools. Agile data engineers adopt agile database tools that enable them to work in an agile manner.
Most importantly, agile data engineers recognize that they need to be agile.
What Agile Data Engineers Do
To understand the role of agile data engineers, let’s consider what they do in practice:
- Agile data engineers work very closely with application developers to implement and support data-oriented development efforts. Agile data engineers work closely with developers, typically supporting a single larger team or several smaller teams as the case may be. Agile data engineers can often be responsible for several data sources (e.g. databases, files, XML structures, and so on) or at least be co-responsible for them. For example, if two development teams access the same database, and each of them have different data engineers, then those people will need to work together to evolve that database over time. To interact effectively with developers, agile data engineers need to learn fundamental development techniques, encapsulating database accessand mapping objects to RDBs (O/R mapping).
- Agile data engineers must work in an evolutionary, if not agile, manner just as application developers do. The biggest potential change for Agile data engineers is that they will need to work in an iterative and incremental manner for with many teams. Modern development processes, such as Scrum, SAFe, or Kanban typically don’t provide detailed requirements up front nor do they focus on detailed models (and certainly not detailed data models up front). They will do some initial requirements and architecture envisioning and then evolve their models over time to reflect their changing understanding of the problem domain as well as the changing requirements of their stakeholders.
- Agile data engineers need to work with operations engineers to take advantage of and to help evolve corporate meta data, standards, and guidelines. When it comes to data, an operations engineer focuses on the physical aspects of data administration such as data source installation, maintenance, back up, restoration, upgrades, tuning/optimization, disaster recovery, and support. Agile data engineers will collaborate with operations engineers to help the team produce work which reflects your organizations overall strategy. They will also want to take advantage of any Master Data Management (MDM) efforts that are currently in place, if any. There is no reason, other than political, why this cannot happen in an agile manner.
- Agile data engineers need to work with enterprise architects to ensure that their work reflects the architectural vision. Agile data engineers will work with your enterprise architecture team, if one exists, to take advantage of existing infrastructure and strategies. Once again, this can also happen in an agile manner.
The Skills of an Agile Data Engineer
To be successful, agile data engineers require the following skillset:
- People skills. Agile data engineers must have the people skills which enables them to collaborate effective with others.
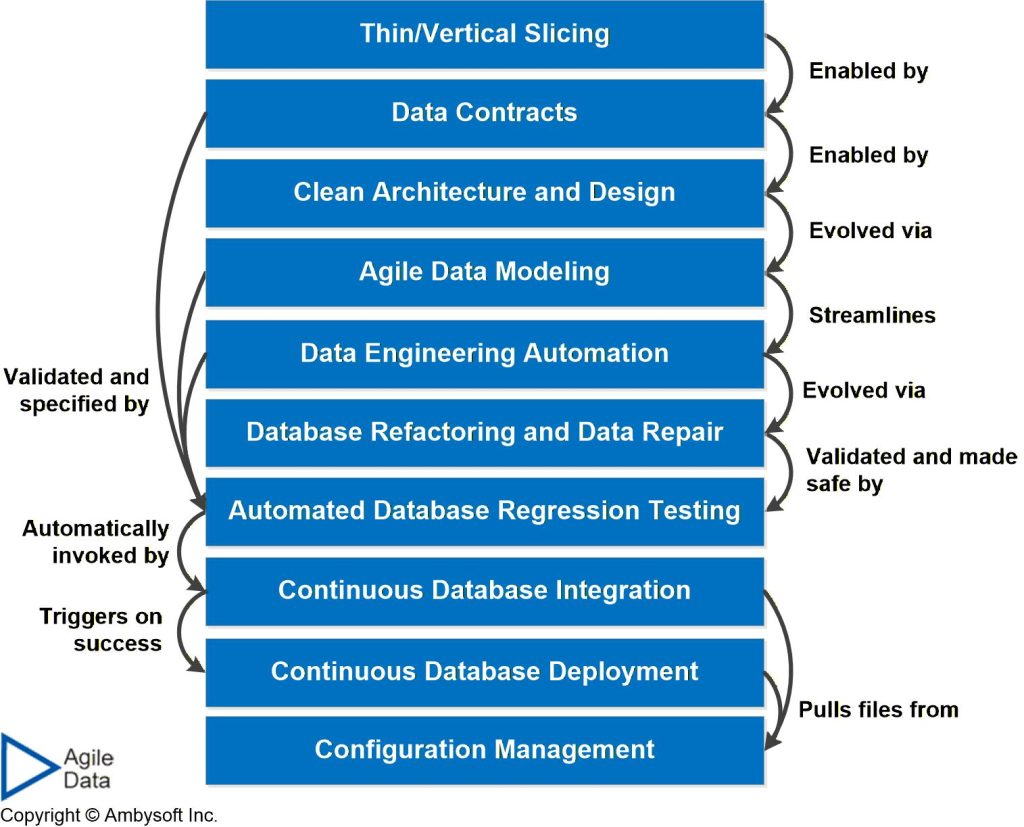
- Technical skills. Agile data engineers need to adopt evolutionary, if not agile, database techniques such as those of the agile database techniques stack summarized in Figure 1.
- Evolutionary development skills. Because agile teams work in an evolutionary (iterative and incremental) manner, agile data engineers must have evolutionary development skills.
- General skills and knowledge. Agile data engineers must have at least a basic understanding of all aspects of the software process and the business domain in which they’re working. Ideally they should be generalizing specialists.
Figure 1. The Agile Database Techniques Stack (click to enlarge).
Related Resources
- Agile data modeling
- Agile Software Development
- Automated database regression testing
- Clean data architecture
- Clean database design
- Configuration management
- Continuous database integration (CDI)
- Data Repair
- Database refactoring
- Introduction to DataOps: Bringing Databases Into DevOps
- The Roles of the Agile Data Method
- Thin slicing: Enabling Continuous DW/BI