Data Quality: An Overview of DQ Techniques
There are many data quality techniques available to you. More accurately, there are many techniques that may lead to improved data quality when they are followed properly. I say this because as you will soon see, some of the techniques included in this article aren’t primarily focused on quality, yet have secondary side effects of improved data quality. The goal of this article is to overview the data quality techniques that I have assessed for their effectiveness in practice.
Data Quality Techniques That Have Been Assessed
There are many potential data quality techniques for you to adopt:
- Clean data architecture. A clean data architecture is one that easy to understand, to implement, and to evolve.
- Data cleansing (at point of use). Data quality problems are fixed by the system that is using the data, often saving a copy of the clean data for later use.
- Data cleansing (via AI). Artificial intelligence (AI)-based tooling is used to cleanse data at point of use.
- Data contracts. A data contract outlines how data is exchanged between two parties, defining the format, structure, and semantics of the data. Data contracts are effectively a data focused contract model.
- Data governance (lean/non-invasive). The goal of data governance is to ensure the quality, availability, integrity, security, and usability of information within an organization. Lean/non-invasive data governance motivates people to do the “right things,” enables them to do so, and then monitors and guides their efforts where needed.
- Data governance (traditional). A command-and-control approach to data governance.
- Data guidance. Standards and guidelines to be followed when developing data-oriented assets (such as databases, data files, business intelligence (BI) outputs, and so on. Data guidance includes naming conventions, data security/privacy conventions, data retention guidelines, data residency guidelines, and so on. Data guidance is often driven by regulatory compliance requirements.
- Data labeling. An artificial intelligence (AI) strategy where the information contents represented by data is indicated. For example, a picture of a cat would be given the label “cat”.
- Data masking. The hiding (masking) of sensitive data, particularly personally identifiable information (PII).
- Data repair. Data quality issues are addressed in the data source itself. Also known as data cleansing (at source) or data quality refactoring.
- Data stewards. An oversight/governance role that is responsible for promoting the quality and fitness for purpose of organizational data. This role is often staffed by mid-level business decision makers.
- Database refactoring. A process by which an existing database schema is evolved in a safe and effective manner through the application of database refactorings. A database refactoring is a simple change to a database schema, such as renaming a table or splitting a column, which improves the quality of the design without changing the semantics (in a practical manner). There are 60+ proven database refactorings.
- Database regression testing (automated).
- Database regression testing (manual). Database testing is the validation of functionality implemented within, and the data values contained within, a database. Database regression testing is database testing done in a regular manner throughout the system development lifecycle, often as part of your continuous integration efforts.
- Defect logging. Regarding data, this is the recording of potential quality problems with the data. Defects are logged so that the owners of the data source have a record of the quality problem so that it may be addressed.
- Executable business rules. Business logic that is invoked to manipulate, and even cleanse, information. Business rules should be highly cohesive, performing one task such as performing a calculation, and loosely coupled to one another.
- Logical data modeling (LDM). LDMs are used to explore the domain concepts, and their relationships, of your problem domain. This could be done for the scope of a single initiative or for your entire enterprise. LDMs depict the logical entity types, typically referred to simply as entity types, the data attributes describing those entities, and the relationships between the entities.
- Master data management (MDM). The primary goals of Master Data Management (MDM) are to promote a shared foundation of common data definitions within your organization, to reduce data inconsistency within your organization, and to improve overall return on your IT investment. MDM, when it is done effectively, is an important supporting activity for enterprise architecture, for enterprise architecture in general, for business intelligence (BI) efforts, and for software development teams in general. Agile master data management is an evolutionary and highly collaborative approach to MDM.
- Physical data modeling (PDM). PDMs are used to design the internal schema of a database, depicting the data tables, the data columns of those tables, and the relationships between the tables. PDMs often prove to be useful on both Agile and traditional teams.
- Review (implementation). A review or walkthrough of your implementation – including source code, data schema, and testing code – by qualified people who were not directly involved with the work being reviewed.
- Review (model). A model review, also called a model walkthrough or a model inspection, is a validation technique in which your modeling efforts are examined critically by a group of your peers. The basic idea is that a group of qualified people, often both technical staff and stakeholders, get together to evaluate a model or document.
- Static schema analysis. An automated evaluation of your schema, including both structural (e.g. tables) and behavioral (e.g. stored procedures), to identify potential quality issues.
- Synthetic training data. An AI strategy where artificially generate data is added to an existing data store to include values that are statistically underrepresented in the original data source. This is an artificial intelligence (AI) strategy to remove bias in machine learning (ML) models.
- Transformation (T in ETL). Data is extracted (read) from a legacy data source, transformed so as to improve it’s quality, and then loaded into another data source.
Other Data Quality Techniques
Other data quality strategies that I may decide to rate at some point in the future include:
- Agile architecture envisioning. Initial, high-level modeling performed at the beginning of an initiative (or programme, or enterprise architecture effort) to identify a viable technical direction for the effort. The goal is to do just enough modeling to drive to the technical vision/strategy, not to create extensive models or detailed documentation. Typically performed in parallel to agile requirements envisioning.
- Agile data modeling. An evolutionary (iterative and incremental) and highly collaborative approach to modeling data. Agile data modeling is the act of exploring data-oriented structures in an iterative, incremental, and highly collaborative manner. Your data assets should be modeled, via an Agile Model Driven Development (AMDD) approach, along with all other aspects of what you are developing.
- Agile enterprise architecture. An evolutionary and highly collaborative approach to modeling, documenting, communicating, and governing architecture for an organization.
- Clean database design. Clean database design is the application of proven heuristics that lead to high quality. With clean database design data structures (such as tables) are loosely coupled and appropriately cohesive.
- Continuous database integration. Continuous integration is a development practice where developers integrate their work frequently, at least daily, where the integration is verified by an automated build. The build includes regression testing and possibly static analysis of the code. Continuous database integration is the act of performing continuous integration on your database assets. Database builds may include the creation of the database schema from scratch, something that you would only do for development and test databases, as well as database regression testing and potential static analysis of the database contents.
- Enterprise data modeling (EDM). Data modeling performed at a cross-system, enterprise/organization-wide level.
- Traditional architecture modeling. Detailed architecture models are created early in a project and then (hopefully) followed by the development team. The data aspect of this model should call out the most appropriate data sources to be used, the domain model to be worked to, and the data conventions to be followed.
- Traditional enterprise architecture. A formal approach to enterprise architecture, including the governance and support of it. Enterprise architecture should inform system architecture, leading to greater consistency and reuse (hence quality) in your organization.
- Non-solo work. An approach to working where two or more people actively collaborate to fulfill a task. Agile examples include the practices of pair programming and modeling with others.
Assessing The Effectiveness of Data Quality Techniques
In How to Assess Data Quality Techniques I describe how to apply the comparison factors captured in Figure 1. In How to Choose the Right DQ techniques I share 10 charts like the one that you see in Figure 2 and how to apply them to choose the best fit DQ techniques for the situation that you face. What I don’t do in either of those articles is describe the techniques that I’ve rated, hence this article.
Figure 1. Factors for comparing data quality techniques.
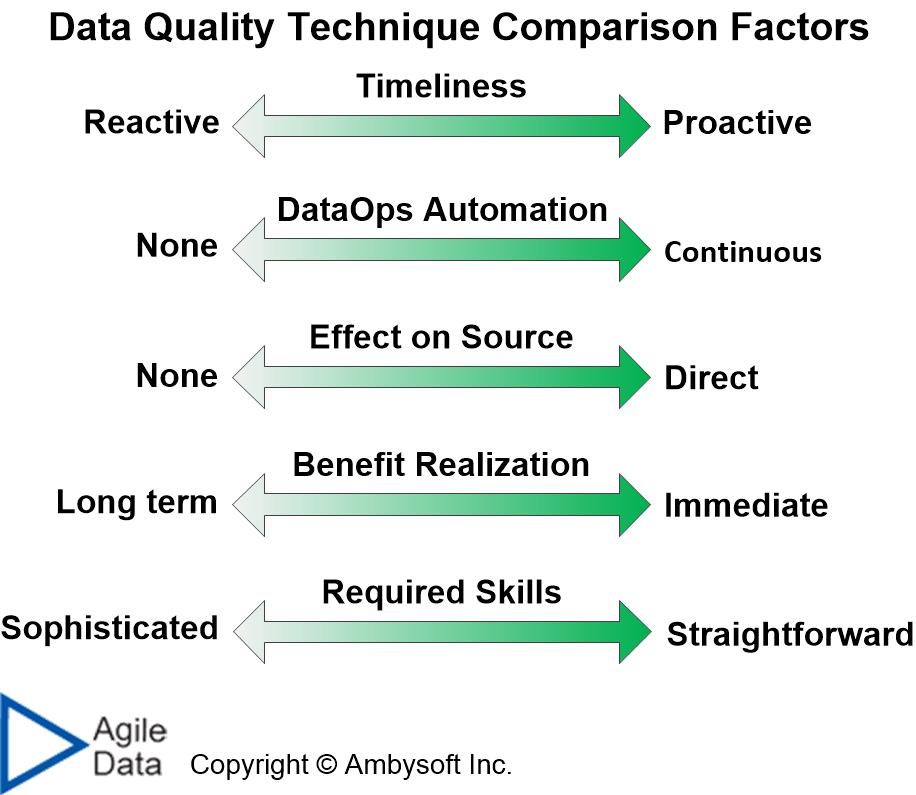
Figure 2. Comparing data quality techniques on effect on source and benefit realization.
There are many data quality techniques for you to choose from. The ones that are “best” for you reflect your context, and that context is unique to you and evolves over time.
Related Resources
- The Agile Database Techniques Stack
- Clean Database Design
- Configuration management
- Comparing Data Quality Techniques
- Continuous Database Integration (CDI)
- Data Debt: Understanding Enterprise Data Quality Problems
- Data Quality in an Agile World
- Data Repair
- Database Refactoring
- Database Testing
- Introduction to DataOps: Bringing Databases Into DevOps
- Test-Driven Development (TDD)
Recommended Reading

This book, Choose Your WoW! A Disciplined Agile Approach to Optimizing Your Way of Working (WoW) – Second Edition, is an indispensable guide for agile coaches and practitioners. It overviews key aspects of the Disciplined Agile® (DA™) tool kit. Hundreds of organizations around the world have already benefited from DA, which is the only comprehensive tool kit available for guidance on building high-performance agile teams and optimizing your WoW. As a hybrid of the leading agile, lean, and traditional approaches, DA provides hundreds of strategies to help you make better decisions within your agile teams, balancing self-organization with the realities and constraints of your unique enterprise context.
I also maintain an agile database books page which overviews many books you will find interesting.

